IN THE EVENT OF AN EMERGENCY THIS SITE IS NOT MONITORED. FOR CURRENT INFORMATION GO TO HTTPS://EMERGENCY.MARINCOUNTY.ORG.
Shaded Fuel Breaks
As communities worldwide grapple with the increasing threat of wildfires, proactive measures are essential to mitigate the potential devastation. One such strategy gaining attention is the establishment of shaded fuel breaks. These breaks serve as a crucial tool in preventing the rapid spread of wildfires, safeguarding both human lives and natural landscapes.
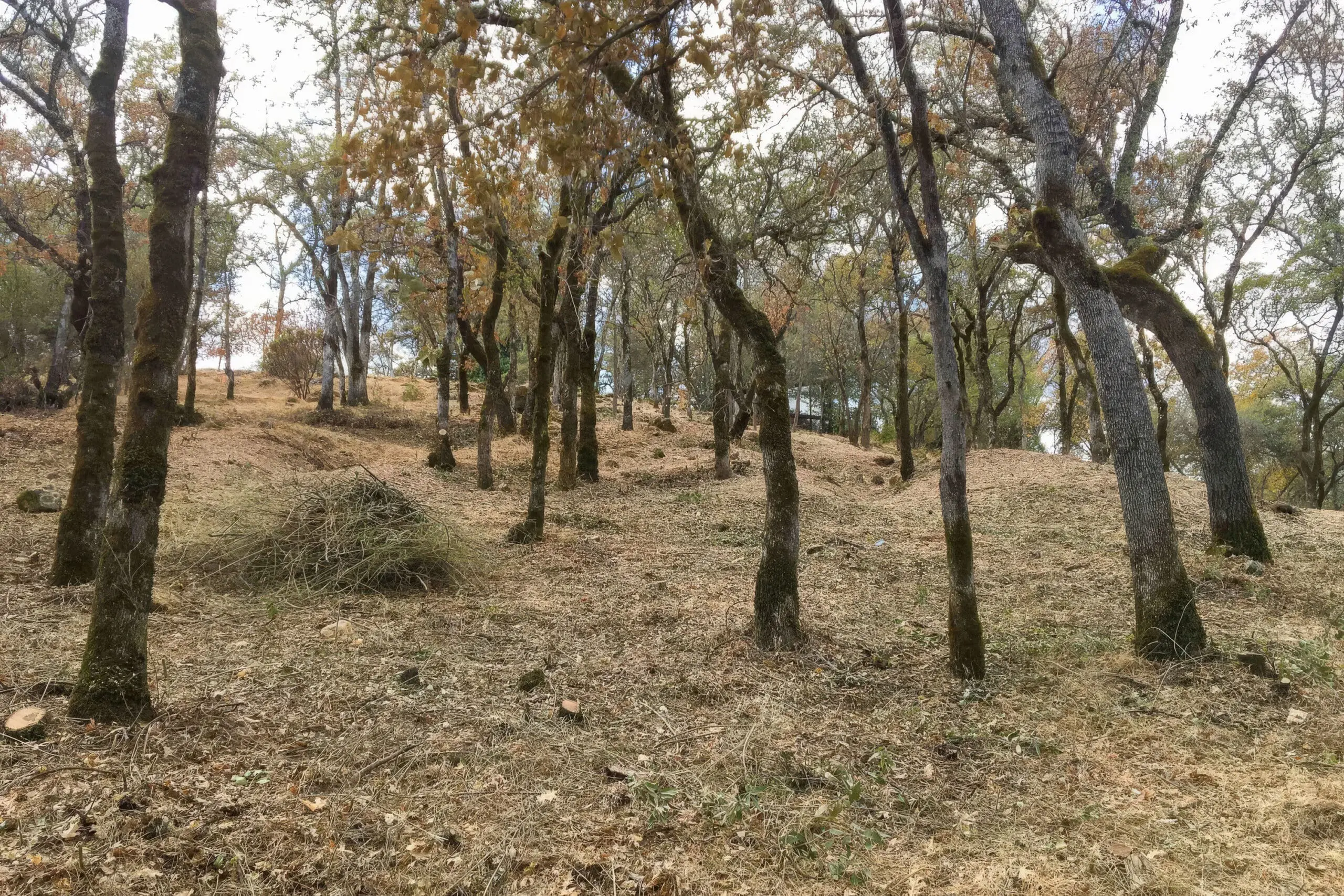

Tall grass, brush, non natives removed to create shaded fuel break and help mature trees thrive
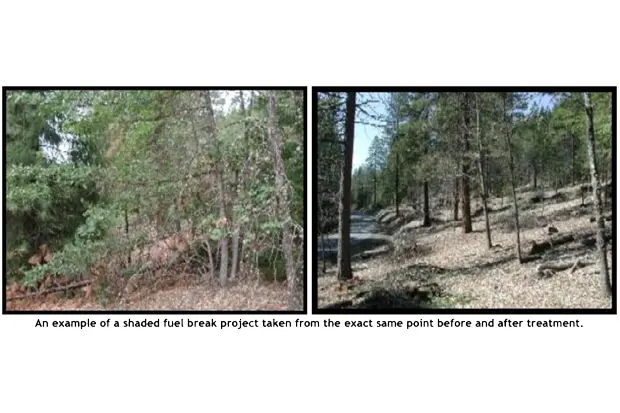

Marin Wildfire Prevention Authority Shaded Fuel Break Project
Shaded fuel breaks involve strategically thinning and modifying vegetation in specific areas to create a barrier that hinders the progression of wildfires. Unlike traditional fuel breaks, which are often devoid of vegetation, shaded fuel breaks maintain a carefully managed mix of live and low-flammability vegetation. This approach not only impedes the fire’s advance but also helps preserve the ecological balance of the area.
Key Components
Benefits of Shaded Fuel Breaks
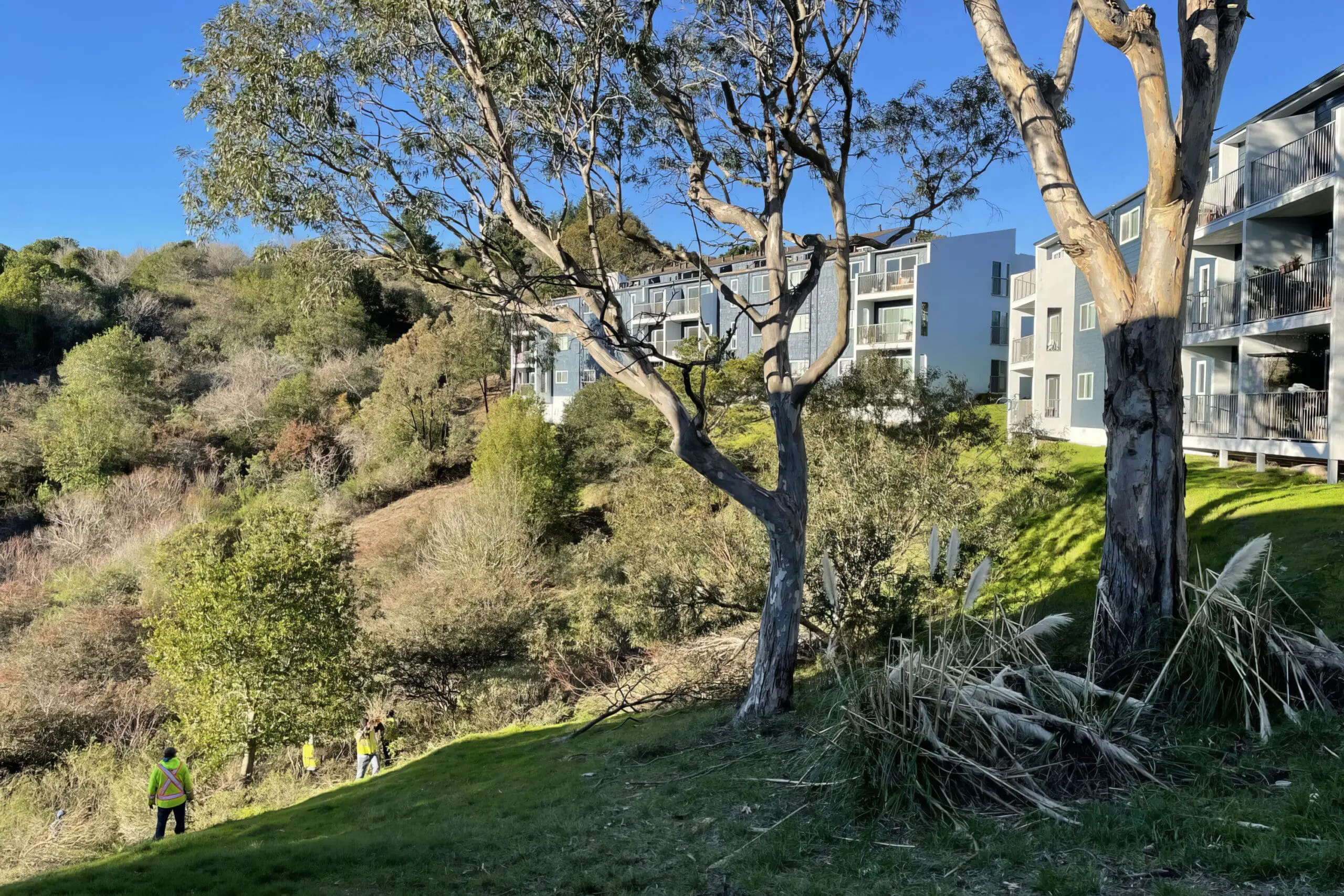
Excellent before and after example of creating a fuel break in souther Marin. Ladder fuels and non native vegetation removed from slopes down hill from apartment buildings. These buildings would have been very vulnerable to wildfire sweeping up hill in heavy vegetation.
Before
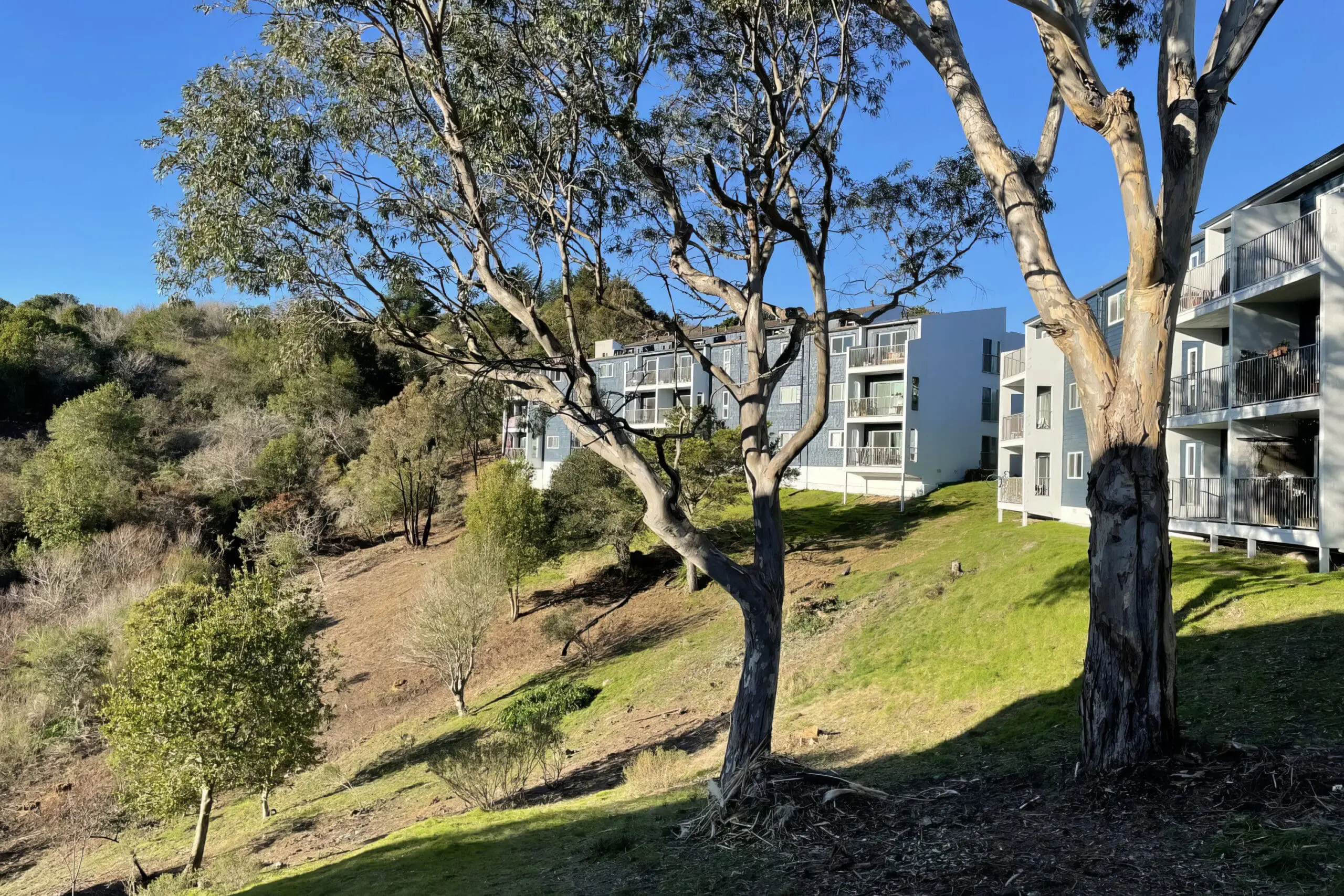


After
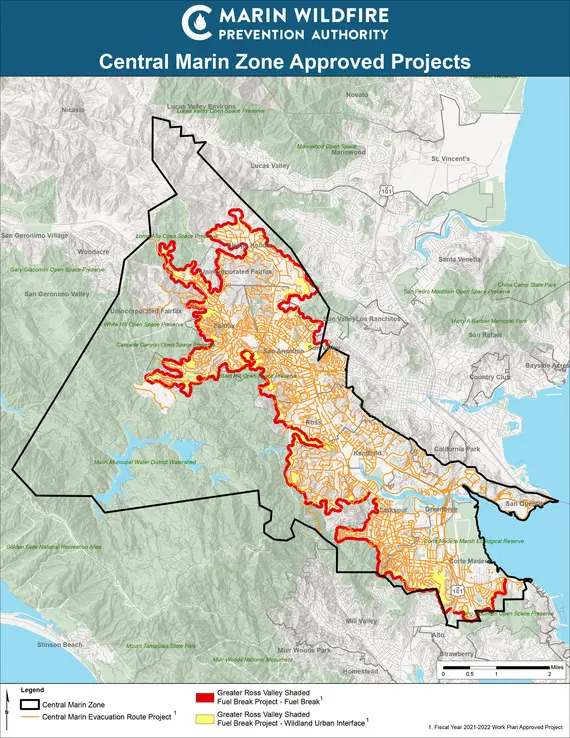
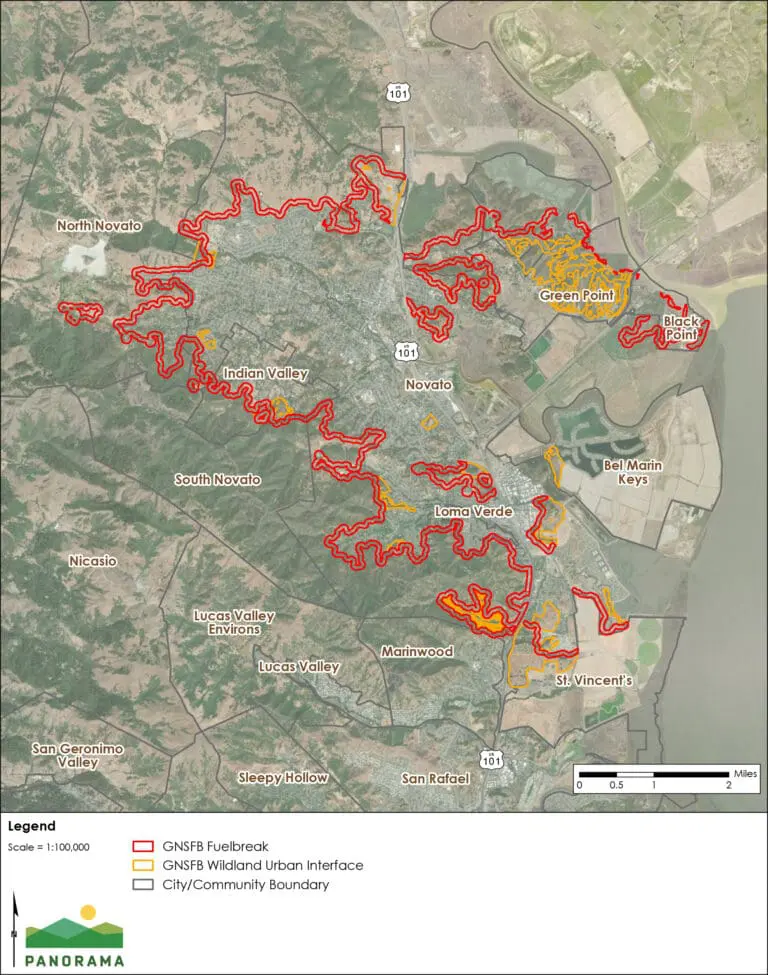
Maps of Large Ross Valley & Novato Fuel Break Projects
In the face of escalating wildfire threats, shaded fuel breaks emerge as a sustainable and ecologically sensitive solution. By combining strategic vegetation management with community collaboration, these breaks offer a practical way to enhance fire resilience, protect communities, and preserve the natural landscapes we cherish. As climate change continues to influence wildfire patterns, shaded fuel breaks represent a forward-thinking approach to safeguarding our shared environment.